Hey there, Pom parents! Taking care of your fluffy buddy means keeping an eye out for some common health stuff.
Your little one might deal with things like wobbly kneecaps (that’s patellar luxation), heart problems, or thyroid issues. Their tiny teeth need lots of love too – these pups can get cavities and gum troubles pretty easily.
🔥 Don’t be me. Seriously. This mistake cost me a small fortune
👉 Find out which pet insurance plans actually cover these common Pom problems before you’re choosing between rent and your dog’s surgery.
Don’t skip the brushing and grooming sessions! They help you spot skin problems, including that pesky Alopecia X (where they lose patches of fur).
Keep your little fluffball from getting chubby by watching what they eat and making sure they get enough exercise – it’s super important for their joints and helps avoid diabetes.
Pop by the vet regularly for check-ups because catching problems early makes them way easier to fix. Knowing what to look out for means your Pom can stay happy and healthy longer!
Common Dental Issues
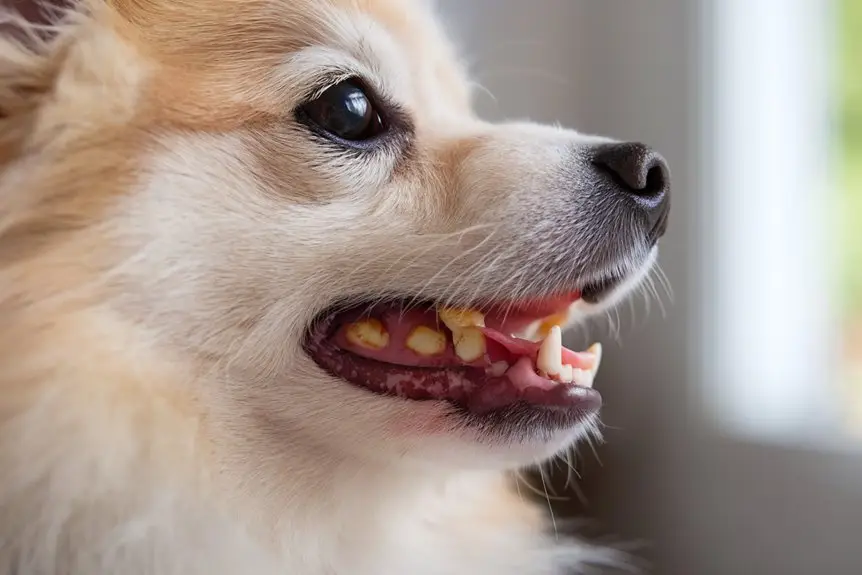

A Pom’s tiny mouth needs lots of care to stop major teeth problems from happening. These little pups easily get gunk built up on their teeth, and they can get tooth decay pretty fast – which means sore gums and stinky breath. If you don’t take care of these problems, your furry friend will have a hard time eating their food.
Make sure to get your pup’s teeth checked by the vet regularly, and get into a good cleaning routine at home. Brushing their teeth every day with special dog toothpaste works best, but doing it three times a week can work too. You can also give your Pom some vet-approved dental treats and small chew toys to help keep their teeth clean. These goodies help fight plaque when you’re not brushing and give some extra cleaning power too. Gum inflammation can develop quickly if dental hygiene is neglected, making preventive care essential for your Pomeranian’s oral health.
Weight Management and Joint Health
Just like good dental care helps your Pom eat better, watching their weight is super important too. When Poms pack on extra pounds, they can run into trouble with their joints – especially that tricky kneecap issue called patellar luxation, where the knee pops out of place. You might spot your pup limping or not wanting to use stairs when their joints are bugging them.
Want to keep these problems at bay? Keep tabs on your furry friend’s weight. Don’t go overboard with food portions and make sure they stay active. Here’s a quick trick – you should be able to feel their ribs when you pet them. If you can’t, they might be carrying a few extra pounds. Talk to your vet about what’s a good weight for your Pom and get tips on the right food amounts. Stick to easy exercises like gentle walks and playing together – these help keep joints healthy without putting too much stress on them. Regular exercise combined with proper nutrition support will help maintain both a healthy coat and optimal weight for your Pomeranian.
Understanding Genetic Health Risks
Ya know how Poms can have some health stuff passed down in their family tree? These little fluffballs might end up dealing with things like wonky kneecaps that pop out of place, or heart sounds that aren’t quite right. Their eyes can give them trouble too – they might slowly lose their vision or get cloudy lenses as they get older.
Keep an eye out if your Pom starts acting sluggish – they could have a thyroid problem that messes with their energy levels. And don’t freak out if you notice some bald patches showing up – that’s probably Alopecia X doing its thing. There’s also this tricky liver problem where the blood takes a shortcut around the liver instead of going through it like it should.
Want to stay ahead of the game? Get your pup’s genes checked out when they’re young and have a chat with your vet about what shows up. That way, you can make sure your fur baby gets exactly the kind of care they need before any problems pop up. Regular veterinary check-ups are essential throughout your Pomeranian’s 12-16 year lifespan to catch and treat these health issues early.
Respiratory and Heart Conditions
Your Pom might struggle with breathing problems, and a collapsed trachea is super common among these little fluff balls. You’ll know something’s up when you hear them coughing, wheezing, or making this weird honking noise. One way to help out is keeping your pup from getting chunky – but if things get really bad, they might need surgery to fix it.
When it comes to heart stuff, these tiny dogs can have their share of trouble. Keep an eye out if your buddy seems extra tired, has a weird heartbeat, or can’t stop coughing – it could mean they’ve got a heart murmur or something more serious going on. A lot of times, these problems run in the family or happen because of wonky heart valves. Make sure you’re taking them to the vet for regular heart check-ups, and they might need some meds or lifestyle changes to stay healthy and happy.
Skin and Coat Care
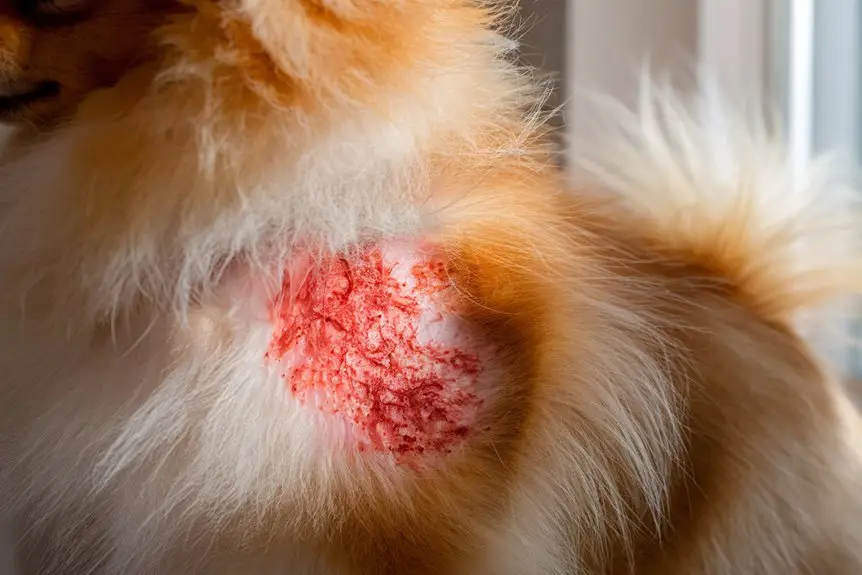
Taking care of that fluffy coat isn’t a walk in the park! Your Pom’s double coat can be pretty tricky to handle, and they sometimes get allergies and skin problems that make them super itchy, red, and even lose fur. Keep an eye out if your little buddy is scratching too much or has patches of missing fur – these could mean something’s up with their health.
Watch out for any skin rashes or hot spots showing up, as your pup might be reacting to something in their environment or food. If you see signs of Alopecia X (that’s when fur falls out evenly on both sides, especially in fixed Poms), get to your vet right away. They might suggest hormone treatments or changing up what your pup eats. To keep that famous fluff looking amazing, stick to regular brushing, feed them right, and jump on any skin problems as soon as you spot them – your Pom will thank you for it! You’ll notice increased seasonal shedding during Spring and Fall when your Pomeranian’s coat naturally adjusts to temperature changes.
Metabolic and Hormonal Disorders
Just like us, your little Pom can run into some tricky body issues, mainly with their metabolism and hormones. Two big ones to keep an eye on are hypothyroidism and hypoglycemia. If your furry friend has hypothyroidism, you might notice them getting chunky, super tired, and losing fur. No worries though – your vet can hook them up with some hormone meds to help them feel better.
Low blood sugar (that’s hypoglycemia) needs quick action when you see your pup getting weak, confused, or shaky. Smart move is to always have some honey or corn syrup ready for those “uh-oh” moments. There’s also this thing called Alopecia X that can make your fixed Pom lose patches of fur. It won’t hurt them badly, but you might need some hormone treatments or diet changes to keep those symptoms in check. Regular veterinary check-ups can help catch these metabolic issues early before they become serious problems.
Vision and Eye Problems
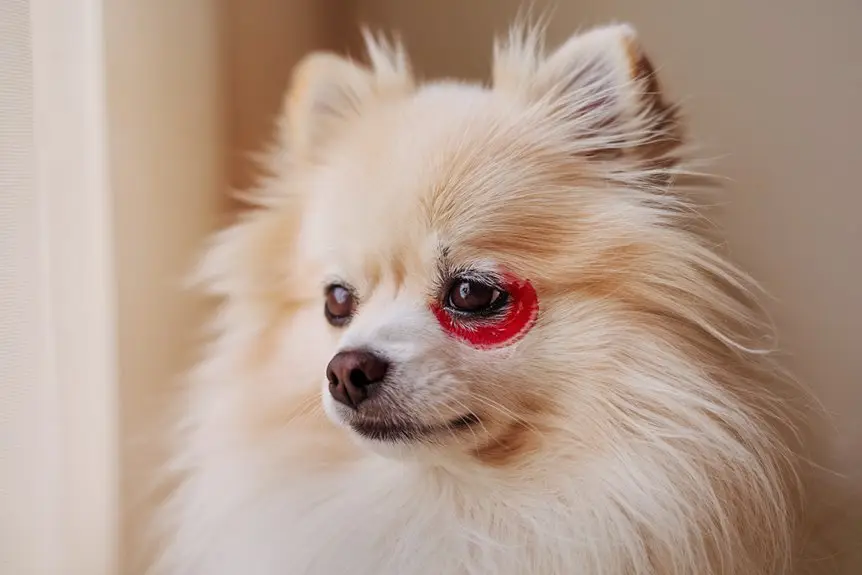

Hey, keeping an eye on your Pom’s cute little button eyes is super important! Your fluffy friend might run into some eye issues, especially progressive retinal atrophy and cataracts – they’re pretty common problems. If your pup has progressive retinal atrophy, they’ll slowly lose their vision. You might notice them getting nervous in dark spaces or bumping into stuff around the house.
With cataracts, you’ll see this cloudy stuff covering their eyes, which can make them totally blind if you don’t get it checked out. Watch if your pup starts walking into furniture, gets scared to jump or go up stairs, or if their eyes look kind of foggy. If you spot any of these signs, get to your vet right away! Regular check-ups can catch these problems early, and your vet might fix things up with some medicine, eye drops, or even surgery if needed.
Early Warning Signs and Prevention
Hey, keeping an eye out for warning signs in your Pom can save you and your furry friend a lot of trouble! Pay attention if your pup’s eating habits change, they’re drinking tons of water, seem super tired, or get unusually grumpy. Don’t brush off things like constant coughing, limping, or breathing problems – these could mean serious stuff like tracheal collapse or joint troubles.
Make sure to check out those teeth regularly! Watch for stinky breath or if they’re avoiding their crunchy food. Also, keep an eye on scratching, patches of missing fur, or red skin – these might mean allergies or hormone issues. Weigh your Pom now and then, because quick weight changes could point to thyroid problems or diabetes. If you see them struggling with stairs or acting confused, get to the vet right away. Your best bet? Regular vet visits and keeping your little buddy at a healthy weight! Excessive drooling or pacing could signal separation anxiety when you’re away from your Pom.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Should I Wait Between Feeding and Exercising My Pomeranian?
It’s best to give your Pom some downtime – around 1-2 hours after meals before any playtime or walks, and about 30 minutes to chill after exercise before chowing down. This way, your pup won’t get an upset tummy or run into any nasty stomach problems.
Can Pomeranians Safely Play With Much Larger Dogs?
Your little Pom may be super brave like a tiny warrior, but letting them play with big dogs needs close watching. Since bigger dogs could hurt them by accident – even during friendly play – it’s smarter to find buddies closer to their size.
At What Age Do Pomeranians Typically Start Showing Signs of Aging?
You’ll start seeing your little Pom getting older when they hit about 7-8 years. Their usual bouncy personality might mellow out a bit, their fur might get some silver streaks, and they could start dealing with stuff like tooth troubles, achy joints, or not seeing as well as they used to.
How Often Should I Groom My Pomeranian During Seasonal Coat Changes?
Hey, you’ll want to brush your Pom every day when they’re blowing their coat in spring and fall. Get in there real good with the brush to tackle that thick undercoat – it’s important to get rid of all that loose fur before it turns into a tangled mess!
What Temperature Ranges Are Considered Safe for Outdoor Pomeranian Activities?
Hey – temps are super important! Keep your Pom’s outside playtime between 45-75°F (7-24°C). When it’s colder or hotter than that, you’ll wanna cut back on the time outside. And during summer, remember to test the ground – if it’s too hot for your hand, it’s definitely too hot for those tiny paw pads!




